Due to a lack of wind resistance while running on a treadmill, the effort of running on a treadmill at 0% incline is less than that of running on a level road at the same pace. Our Tristar chart can help you get an approximate equivalent effort for zones between running on a treadmill at different paces and inclines and running outdoors on a level surface. Learn how you can use the normalized graded pace incline chart to target different pace zones with slower uphill running efforts.
Running
Run training block introduction
Athlete Resources, Running, Training Peaks, ★★★, CTL
Estimating key continuous training loads for stand alone running (CTL's)
Tristar Athletes, In this table we present the peak continuous training load score for each athlete. Recall that CTL score is a rolling average of your daily training stress score over the past 42 days. Your peak CTL is the highest CTL you achieve in a period of training. The numbers in this table help you select your training hours and load that’s best for you and your ability.
★★★ Staying injury free on your run
Running as a sport is highly demanding and for most endurance athletes from time to time it lands them in injured territory throughout their career. Unlike swimming and cycling which can be forgiving when you go too hard, running has a higher cost when it comes to the injuries we see. Our coaches provide our top tips for your run and how to stay fast and injury free.
★★★ Tristar Athletes stand alone run pacing and guidelines for training
Art of the long run
Run form correction: "Over-striding"
Running Power Analysis - A hilly trail run in Honduras - Jose Alvarado's pacing review
★★★ Running cadence
★★★ D.Y.O.T ⚠️ "Doing your own thing"
★★★ Heal drop for running
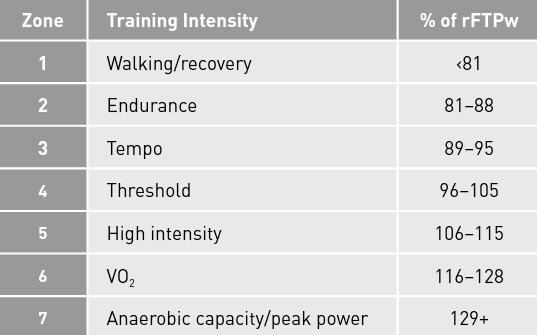
★★★ Ⓦ Running power FTP power defined (rFTPw)
Testing your power in running periodically is important to you training and training zones working with your Tristar Coach. While power in running varies less so than cycling power, keeping an accurate rFTPw (or threshold power. r = “running” and Pw = power. rFTPw) is important towards determining your total load and intensity of your program.
rFTPw NOTES and best practices
One of the major advantages to running with power is that we can clearly define your intensity.
rFTPw is a strong indicator of your race potential and overall potential.
it is the metric used to calculate all intensity in your Tristar plan and program.
All of your run power zones are calculated off this single number.
Do you need to test all the time? No, you can use running data from races and or training to support your rFTPw.
if you switch from one run powermeter manufacturer to another recognize your rFTPw will be different and then you would want to retest.
Tristar testing sets for power; We use two power tests, one which is shorter call the “3/9” TEST, and a “30min run TT (Time Trial)”. The 3/9 test is shorter and does not require as much recovery however the accuracy for the 30min run TT may be better depending on your ability to pace. Your coach will key you in to which test is best for you, your goals and plan. Note; during your testing you will also find your rFTPa (r = run, F = Functional, T = Threshold, Pa = pace) which is helpful when learning how to run at a goal speed or effort beyond power. You will have both FTP’s set in training peaks.
Races: races 5K-13.1mi road races can help determine your rFTPw depending on your ability and time it takes to do each race distance. Example, slower athletes may use 10K as their rFTPw proxy.
Run rFTPw changes regularly. When you stop training threshold power in running will drop, with extended detraining lowering your rFTPw will be critical. Conversely, when you are training a lot at just below or just above run threshold power you may need to update and increase your rFTPw.
What happens if you don’t have an accurate rFTPw? …When set too low this can overstate your actual fitness and your gains may not be as great as they could be in training. … when set too high this can underestimate the total training load and you can get sick or injured.
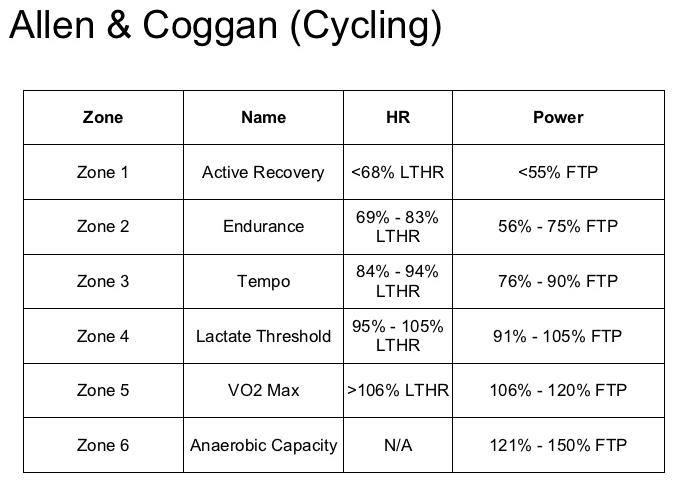
★★★ Running with power vs biking with power
For those Tristar Athletes familiar with bike power zones we have presented the main similarities and differences below to running with power and biking with power.
Similarities
Both use FTP (functional threshold power)
Both have their own unique % of FTP that the zones are made up of.
Both have an absolute advantage for training, a watt is a watt. A measurable output.
Both are helpful for targeting races and for yearly planning.
Both can be used to pace more accurately than heart rate, pace or perceived effort alone.
Both need to be calibrated regularly and the FTP (hour of power or threshold) updated regularly to ensure accuracy.
Run and Bike power zones side by side
Comparison to rate of perceived effort.
Differences
Run power is a more complex measurement as it has two power outputs measure; form power and horizontal or “power that moves you forwards.”
This extra power data can help with form and speed. (Form is crucial to run economy and speed.)
Lower power zones for running tend to be higher as a % of FTP compared to cycling. For example 85% for run power is middle of zone two where as for cycling this is the middle of zone 3.
More power does NOT mean you will necessarily run faster….more power in cycling generally does. Running with greater form (or lowering form power) and increasing stiffness equates to running faster.
Due to the above; We must be observant of both horizontal and form power at all times. As an athlete you should not blindly train by power or zones but rather zones + form efficiency.
The goal should be to maximize your speed/watt.
New to power? Start by focusing on being efficient at slower powers and paces before moving on to harder efforts and work.
With run power you should chart/track your baseline efficiency numbers for each race pace effort you are trying to accomplish. Example; perhaps you have a form limiter when you are running slower? (know your EI, or efficiency index) If you are training for a slower marathon or Ironman marathon for example and your form power is high at slower efforts vs faster there is run form work to be done there. That form work should come before training at a specific wattage or power zone.
running power zones (Jim Vance) vs bike power zones (ALLen and cogan).
★★★Running with Power: Leg stiffness
When Tristar athletes are running rarely do they think about their legs as “stiff” or as “springs” that recoil and return energy. Much of the time we think about how hard we are running or perhaps our form but one area that can help to improve your running speed is the idea that how well you will ever run is based on “leg spring stiffness or “LSS”.



